Soil QULTIVO
QULTIVO can be used to decompose the residue left in the field after harvest or harvest, and to prepare the field for sowing or cultivating any plants in large-scale crops, field, orchard and under cover, as well as in nurseries, parks and green areas, both in crops ecological and conventional.
To improve the physico-chemical properties and indicators of all soil types, it is best to use QULTIVO twice a year during soil treatment:
- in autumn - after harvest or harvest to process the residue in the field, their further organic mineralization.
- in spring - with the introduction of mineral fertilizers into the soil or during planting or sowing.
AUTUMN
The amount of QULTIVO per 1 ha of field depends on the amount of plant residues after harvesting, and depending on the plant species is as follows:
If after the harvest on 1 hectare of field there is:
- 1 ton of plant residues, use 1 liter of QULTIVO per 200 liters of water per 1 ha
- 2 tons of plant residues, 2 liters of QULTIVO should be used for 200 liters of water per 1 ha
- 3 tons of plant residues, use 3 liters of QULTIVO per 200 liters of water per 1 ha
- 10 tons of plant residues, use 10 liters of QULTIVO per 200 liters of water per 1 ha
We recommend adding 10 kg of urea per 1 ton of residue to the resulting mixture.
So prepared mixture should cover the soil on 1 ha using a sprayer or a slurry tanker. The treatment can be performed e.g. after rainfall so that QULTIVO can get to the root zone of plants as soon as possible, you can also use more water than 200 liters per 1 ha for dilution if necessary concentrate.

SPRING
Activation, soil remediation.
Approximately 20 days before planting seedlings or sowing seeds per 1 ha of field, depending on the quality of the soiluse 1 to 5 liters of QULTIVO concentrate diluted in 250 liters of water. After 14 days (at most 30 days) the soil should be plowed.
APPLICATION TABLE QULTIVO
The amount of QULTIVO concentrate and the amount of water needed to prepare the solution and the number of treatments for the different crops.
Plant group or application method | Plant group or application method | Plant group or application method | Plant group or application method | Dose concentrate QULTIVO | Number of treatments | The amount of water in liters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
FOR THE SOIL IN AUTUMN | To the soil | After the harvest, in order to properly distribute the plant residues remaining in the field | Depending on the remaining biomass in the field, e.g .: | • 1 liter of fertilizer per 200 liters of water for 1 ton of residue; • 2 liters of fertilizer, 200 liters of water for 2 tons of residue; • 5 liters for 200 liters of water for 5 tonnes of residue. | 1 | 200 |
FOR THE SOIL IN SPRING | To the soil | Depending on the quality of the soil | about 2 liters per 1 ha | 1 | 250 | |
PLANTS AGRICULTURAL, CEREALS | FOLIAR SPRAYING | 1 liter per 1 ha | 1 - 3 | 200 - 250 | ||
SEEDS | Soaking | 1 liter / 1 tone | 1 | 10 | ||
PLANTS | Soaking | 0,25 liter | 1 | 15 | ||
ORCHARD PLANTS | To the soil | 3-4 weeks before planting plants | • 2 liters per 1 ha or • 20 ml per 100 m2 | 1 | • 400 or • 4 | |
To the soil | In orchards and plantations in early spring | • 2 liters per 1 ha • 20 ml per 100 m2 | 1 | • 400 • 4 | ||
FOLIAR SPRAYING |
| • 1 liter per 1 ha • 10 ml per 100 m2 | 3 - 4 | • 400 • 4 | ||
PLANTS DECORATIVE | To the soil | 3 - 5 days before planting in the ground | • 2 liters per 1 ha • 20 ml per 100 m2 | 1 | • 400 • 4 | |
Fertilization | Plants grown in the ground | Young or weak growing plants | • 1 liter per 1 ha • 10 ml per 100 m2 | 1 - 3 | • 400 • 4 | |
Fertilization | Plants grown in the ground | Older or vigorously growing plants | • 2 liters per 1 ha • 20 ml per 100 m2 | 1 - 3 | • 400 • 4 | |
Fertilization | Plants potted and balcony | April to October | 2 - 3 ml | every 14 to 21 days | 1 | |
Fertilization | Plants potted and balcony | In winter | 2,5 ml | once a month | 1 | |
FOLIAR SPRAYING | 2,5 ml | 3 - 4 | 1 | |||
LAWNS | To the soil | Early spring or fall | 3 - 5 days before setting up the lawn | • 2 liters per 1 ha • 20 ml per 100 m2 | 1 | • 400 • 4 |
Fertilization | • 2 liters per 1 ha • 20 ml per 100 m2 | once a month | • 400 • 4 | |||
FOLIAR SPRAYING | • 0,5 liter per 1 ha • 5 ml per 100 m2 | 3 - 4 | • 200 • 2 | |||
PLANTS VEGETABLE | To the soil | before cultivation in the ground | 5 - 10 days before sowing seeds or planting seedlings | • 2 liters per 1 ha • 10 ml per 100 m2 | 1 | • 400 • 2 |
Fertilization | vegetables grown in the ground | after emergence, after the first proper leaves have formed and the seedlings have taken root | • 0,5 liter per 1 ha • 5 ml per 100 m2 | 1 | • 200 • 2 | |
Fertilization | vegetables grown in the ground | older and stronger plants | • 1 liter per 1 ha • 10 ml per 100 m2 | every 14 to 21 days | • 200 • 2 | |
Fertilization | vegetables grown under covers | during the growing and fruiting season | • 0,5 liter per 1 ha • 5 ml per 100 m2 | every 7 to 14 days | • 200 • 2 | |
Fertilization | vegetables grown under covers | species with strong growth (tomato, cucumber, pepper) | • 1 liter per 1 ha • 10 ml per 100 m2 | every 7 to 14 days | • 200 • 2 | |
FOLIAR SPRAYING | • 0,5 liter per 1 ha • 5 ml per 100 m2 | 2 - 4 | • 200 • 2 |
Use of concentrate QULTIVO:
Recommendations:
- It is recommended to apply to all types of soil, especially poor, loamy, saline and sandy soils!
- Perform spraying when the air temperature is between +5 and + 25 ° С
- Use the finished product at dawn or after sunset - in the morning or in the evening, when the wind is low.
- Do not use on frozen, flooded, water-saturated, snow-covered soils and during rainfall. Frozen soils shall not be considered to be those which thaw at least the surface during the day.
- Apply to the soil simultaneously with watering many times throughout the growing season, at least two weeks apart (at least 14 days). The last spraying should be done no later than 2-3 weeks before harvesting!
- Apply both alone and in combination with mineral fertilizers or against their background (with such a combination, the efficiency factor in the form of obtaining an increase in yield increases significantly).
- Do not exceed the recommended doses.
Preparation of the working liquid:
- Shake the container well before opening and measure the required amount of fertilizer.
- Partially fill the sprayer tank with water (if possible, use warm water at a temperature of +20 to + 25 ° С) and pour the measured amount of fertilizer with the agitator turned on.
- Fill the water tank with water while stirring.
- Use the prepared working fluid immediately after its preparation.
- The fertilizer can be used together with plant protection products, after prior testing of their miscibility, as a result of which no sediment or other insoluble element is formed.
Storage conditions:
- Store in a cool and dark place, in original packaging, at a temperature of + 5 ° С to + 30 ° С
- Dispose of unused fertilizer packaging after the expiry date.
- Shelf life of 2 years.
Precautions:
- When working with fertilizer, observe the generally applicable hygiene and safety rules.
- Use protective gloves.
- In the event of eye contamination, rinse thoroughly with water and, if necessary, consult a doctor.
- The product is not suitable for consumption, keep away from children.
FOR SOIL AND LEAVES

The main indicator of soil fertility is the content of humus, the most important component of organic matter in soil. Soil fertility has deteriorated rapidly in recent decades. Frequent overdose of mineral fertilizers leads to unjustified losses, soil and plants do not absorb them, most of them end up in groundwater, polluting the environment and increasing the surface of acidic soil. This is the result of ignoring the laws governing soil formation, the nature of soils. Keeping soil fertility is only possible with strict adherence to and maintaining a certain balance of organic and inorganic substances in soils.
Over time, a decrease in soil humus content was observed.
A drop of this indicator by only 0.1% leads in various environmental and economic conditions to a drop in yield to 100 kg of ready crop from 1 hectare. At the same time, plants can use 20-30 kg of nitrogen per 1 ha for 1% humus.
The objective right of agriculture is violated – the right to return, the soil must completely recover everything that comes from it and what is not constantly replenished from natural sources. In the current situation in agriculture, a large part of the crop is created by mobilizing soil fertility without compensation of nutrients carried out with the crop – as a result, a constant negative balance of nutrients depletes the soil, destroys humus.
The lack of traditional forms of organic fertilizers means that we find new types of organic materials and incorporate them into modern agricultural technologies. One of these solutions is a microfertilizer and a complex stimulator, growth regulator, soil remediation, based on humic substances – QULTIVO.
QULTIVO LIFE AND SOIL
QULTIVO – acts as a strong catalyst for: biochemical processes in soil, its biological activity, primarily because the organic matter of humic substances is used by soil microflora as a source of energy and nutrients.
QULTIVO stimulates the growth and development of beneficial microorganisms (spore bacteria, mold fungi, cellulosic bacteria) in soil during its use as a post-harvest recultivator. As a result, the decomposition of organic residues and wood (cellulose, hemicellulose, proteins, lignin) is more intense, the processes of humification are accelerated, the soil is enriched with humus. The application of QULTIVO after a year causes not only quantitative but also qualitative changes in humus in soil, the resulting humus has high biological activity, its presence improves the physical and chemical properties of the soil.
To maintain soil fertility, it is important to fully utilize the potential of QULTIVO, in accordance with the application rates described below.
QULTIVO application rates:
I termin – in the spring after plant vegetation starts,
II termin – in autumn before the end of vegetation,
– applies to all periods of 1 to 5 or more liters per 1 ha after dilution in 200 l of water. The liquid prepared in this way should be covered with an area of 1 ha using a sprayer or a slurry tanker. Thanks to this, QULTIVO can get to the root zone of plants the fastest.

NOTE the amount of QULTIVO concentrate per 1 ha depends on the amount of harvest or harvest residues.
If after the harvest on 1 hectare of field there is:
- 1 ton of plant residues, use 1 liter of QULTIVO per 200 liters of water per 1 ha
- 2 tons of plant residues, 2 liters of QULTIVO should be used for 200 liters of water per 1 ha
- 3 tons of plant residues, use 3 liters of QULTIVO per 200 liters of water per 1 ha
- 10 tons of plant residues, use 10 liters of QULTIVO per 200 liters of water per 1 ha
Cereal straw has a high humification factor. For this purpose, it should be crushed and evenly distributed throughout the field, preferably before plowing, treated with QULTIVO, and then re-packed into the ground (straw anchorage depth 6-12 cm)!
Burning dry residues causes huge damage to agriculture! With a single burn of winter wheat stubble, with a capacity of 3000-4000 kg per 1 ha, the amount of organic matter of the stubble and the surface layer of soil that can be compensated only by adding 15 tonnes of manure per hectare is destroyed. Minimal calculations show that in order to reduce the decrease in humus content, it is necessary to leave at least 30% of soil covered with plant residues, the best solution is 100% of crop residues!
In the structure of arable areas, the specific weight of crops should be:
- perennial grasses with an area of at least 16-20% of arable land,
- legumes – peas, wikis, etc. – not less than 15-16%,
- net pair – not less than 10%.
QULTIVO’s processing of green manure plants: lupine, sweet clover, peas, rapeseed, mustard, buckwheat etc., followed by their deep incorporation into the soil, will ensure a significant build-up of humus!
QULTIVO AND SOIL TYPES
QULTIVO is recommended for all soil types also:
- on alkaline soils with low iron content;
- on sandy, sandy loam soils with a low content of organic matter (humus);
- on acidic podzolic soils with low humus content, simultaneously with liming;
- on salt soils (salt marshes);
- on calcareous soils..
For each of these soil types, the use of QULTIVO gives:
- removal of plant poisoning by clogging the root nutrition environment (neutralizes the toxic salinity effect 6-10 times larger than normal);
- increases the overall indicators of porosity and moisture capacity (decrease in soil density)
- increases the content of total nitrogen, calcium and magnesium;
- improves acid sorption and properties;
- activates the activity of soil microorganisms;
- transforms mineral elements into a form accessible to plants;
- increases soil enzymatic activity;
- increases the mobility of nutrients in the soil;
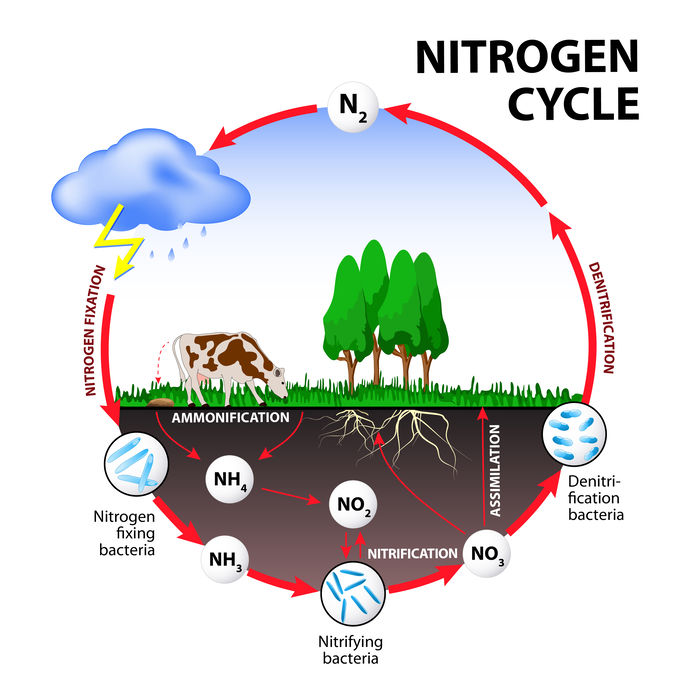
- increases photochemical nitrogen binding and availability of organic soil nitrogen for plants;;
In different soil types, the percentage of humus varies from 1% to 20%.
The QULTIVO action aims to increase soil fertility and increase yields.
The QULTIVO action aims to increase soil fertility and increase yields
- Brown and soda-podzolic soils – in areas north of the Polish mountains (Silesia and Lesser Poland) – 1.0-2.5%
- Sandy, mugwort (containing leaking valuable soluble minerals) and requires use in agriculture for fertilizers – 0.8-2.0%
- Peat (along river valleys) – 1-6%


The use of QULTIVO improves the physical, physico-chemical properties of soils, air, water and thermal conditions. QULTIVO together with mineral and organic-mineral soil particles forms a soil-absorbing complex that determines its absorption capacity. The introduction of QULTIVO leads to the fact that humic substances, surrounding, sticking together mineral particles of the soil, contribute to the creation of a very valuable waterproof lump-granular structure that improves water flow and the ability to retain water in the soil, its air permeability.
The particles of humic substance QULTIVO enter the soil structure; in their presence, the capacity to exchange land increases rapidly. The adsorbed forms of nutrients do not bind to the soil, are not leached out by water and are in a state accessible to plants. In the future, plants use these adsorbed substances more intensively than from soil solution. All useful microelements, which are metals, form chelate complexes with QULTIVO in the soil, and then penetrate the plants, providing them with food, and iron and manganese are absorbed only in the form of humic complexes.
Humic substances in QULTIVO, introduced into the soil, contribute to the preservation of nutrients in it and their more rational use. During soil processing with QULTIVO, the consumption of legumes and cereals increases: phosphorus from soil by 20-25%, potassium by 23-25%, the content of mobile phosphorus in soil increases by 1.5-2 times, ammonium nitrogen by 2-2 , 5 times, improves the supply of nutrients from the soil to plants, preventing leaching of easily soluble potassium, nitrogen salts.
QULTIVO MICROFLORA AND SOILS
The action of QULTIVO in soil is not limited to action on microorganisms that are “responsible” for the accumulation of humus. The introduction of QULTIVO into the soil significantly intensifies the activity of various groups of microorganisms with which the mobilization of soil nutrients and the conversion of potential fertility into effective ones are closely related. Due to the increase in the number of silicate bacteria, there is a constant replenishment of potassium metabolized by plants.
QULTIVO increases the number of microorganisms in the soil that break down insoluble mineral and organic phosphorus compounds. After using QULTIVO, the availability of soil with assimilated nitrogen reserves is improved: the number of ammonium bacteria increases from three to seven times. By improving the living conditions of free-living bacteria after adding QULTIVO, their ability to bind molecular nitrogen from the atmosphere increases almost 10-fold. QULTIVO stimulates nodule bacteria of the genus living in symbiosis (shared housing) with legumes (alfalfa, lupine, clover, peas, vetch, beans), as well as rhizospheric microorganisms living in the excretion zone of non-legume roots.
Thus, QULTIVO in soil stimulates the activity of all types of microorganisms, binding nitrogen in the atmosphere and making it digestible for cultivated plants.
QULTIVO contributes to the significant activation of those groups of microorganisms that are involved in the mineralization of organic substances. As a result, the soil is enriched with available nutrients. The breakdown of organic matter causes the formation of a large amount of organic acids and carbon dioxide. Under their influence, inaccessible mineral compounds of phosphorus, calcium, potassium and magnesium are transformed into forms available to the plant.
HUMATES AND ECOLOGY OF AGRICULTURAL LAND
Humic substances in QULTIVO, which are the main active substance, have the ability to gel. Due to this quality, after the soil is treated with the drug, its ability to retain moisture for a long time increases.
Considering that today climate change associated with global warming around the world is a big problem with creating a moisture reserve in the soil of agricultural enterprises that grow plants, this property of QULTIVO is becoming particularly important. On the other hand, thanks to the introduction of QULTIVO, the same soils retain satisfactory properties for longer during intensive irrigation, including irrigation, using large doses of mineral fertilizers.
Analysis of soils on which preparations containing humic substances were used shows that these soils are more resistant to the effects of chemical contaminants: radionuclides, heavy metals (lead, mercury, chromium, cadmium, etc.) and pesticides. In an era of urbanization and arable farming on arable land near large industrial areas, this is more than important.
QULTIVO binds harmful compounds, forming complexes insoluble in soil solution, their penetration into plants, soil and groundwater becomes impossible! In technogenic zones, watering the soil with QULTIVO solution (at a concentration of 1-3 liters per 1 ha) significantly increases the biological activity of the soil and promotes the resistance of plants to harmful emissions from industrial plants.
Modern plant production is impossible without the use of various pesticides necessary to control weeds, pests and plant diseases. However, the use of these drugs causes a number of negative phenomena due to their accumulation in soil: the soil microflora is lost and the physiological functions of plants are disturbed. Poisons accumulate in agricultural products, negatively affecting human life. The use of QULTIVO in soil stimulates the activity of microorganisms and contributes to the accelerated degradation of pesticides in the soil. At the same time, the resistance of plants to these chemicals increases, and the rate of poison degradation in plant cells increases.
Introduction of QULTIVO into the soil removes the negative effects of high doses of mineral fertilizers, especially nitrogen fertilizers.






